Lotto Sport Science Chair: Influence of polyphenols on exercise, recovery and the brain
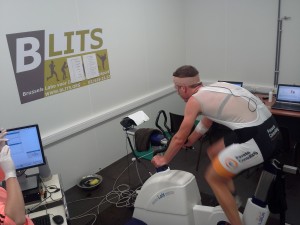
Evidence shows that moderate physical activity has many beneficial health effects, such as decreasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, cancer, obesity and hypertension. Acute moderate intensity and high-intensity exercise increase cerebral blood flow and can improve cognitive function, especially processes requiring executive control. Besides the impact of exercise on cognitive function, nutritional supplements can influence cognitive function as well. In particular, the intake of polyphenols has been associated with improved cognition, but it has to be recognized that the source, quantity and bioavailability of the consumed polyphenols highly influences its beneficial effects.
Despite exercise-related health benefits, exhaustive exercise can induce oxidative stress and increase inflammatory responses. Recent evidence shows that polyphenols exert beneficial effects by an improved endothelial function, the ability to suppress oxidative and inflammatory stress.
For polyphenols, it remains unclear whether their antioxidative and vasodilatory properties can play a role in improving exercise performance and post-exercise recovery. This study aims to examine the acute and longitudinal impact of polyphenol intake on exercise-induced alterations in cognitive functions, to investigate whether polyphenol intake will influence oxidative stress and inflammation and to explore effects of intake of high- dosage polyphenols on post-exercise recovery.
Auteur: Lieselot Decroix
« Retour au sommaire